Aircraft Carrier Size Comparison

Introduction to Aircraft Carriers

Aircraft carriers are the centerpiece of a nation’s naval power, serving as a mobile airbase that can be deployed to any corner of the world. These vessels are designed to carry, arm, and deploy aircraft, playing a critical role in military operations. The size of an aircraft carrier is a significant factor in determining its capability, as it influences the number of aircraft it can carry, the type of aircraft it can handle, and its overall combat effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the world of aircraft carriers, exploring their various sizes, classes, and the implications of these differences.
Classes of Aircraft Carriers

There are several classes of aircraft carriers, each with distinct characteristics and capabilities. The main classes include: - Light Aircraft Carriers: These are the smallest and most basic type of aircraft carrier. They are designed to carry a limited number of aircraft and are often used for training, support, or in secondary roles. - Medium Aircraft Carriers: This class offers a balance between size and capability. Medium carriers can support a wider range of aircraft and are more versatile than light carriers. - Heavy Aircraft Carriers: The largest and most advanced type, heavy aircraft carriers can carry a significant number of aircraft, including fighter jets, bombers, and helicopters. They are equipped with sophisticated systems for aircraft launch and recovery. - Supercarriers: The largest of all, supercarriers are a subclass of heavy aircraft carriers, distinguished by their enormous size, advanced technology, and large air wings.
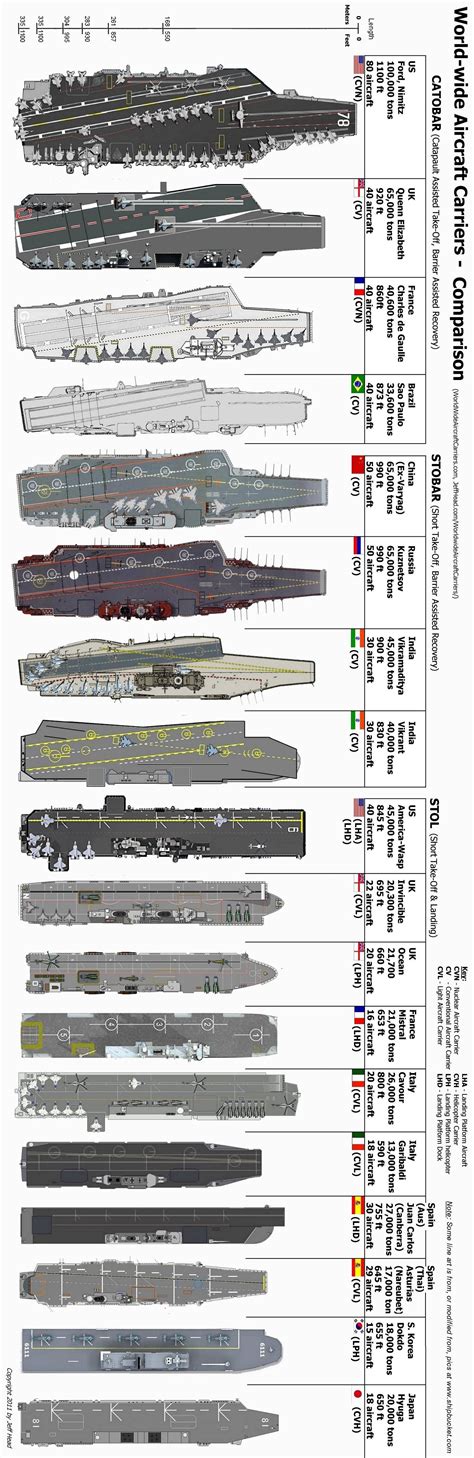
Size Comparison of Notable Aircraft Carriers

The size of an aircraft carrier can vary greatly, with lengths ranging from approximately 200 meters for the smallest carriers to over 300 meters for the largest supercarriers. The beam (width) and draft (depth in the water) also vary significantly. Here is a comparison of some notable aircraft carriers:
| Aircraft Carrier | Length (meters) | Beam (meters) | Draft (meters) |
|---|---|---|---|
| USS Gerald R. Ford (US) | 337 | 78 | 11.3 |
| INS Vikramaditya (India) | 284 | 60 | 8.5 |
| Charles de Gaulle (France) | 261.5 | 64.36 | 9.5 |
| USS Kitty Hawk (US) | 323.8 | 76.8 | 11 |

Factors Influencing Aircraft Carrier Size
Several factors influence the size of an aircraft carrier, including: - Aircraft Type and Number: Larger carriers can accommodate more and larger aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters. - Technology and Design: Advances in technology can allow for more efficient use of space, enabling smaller carriers to have capabilities similar to those of larger ones. - Mission Requirements: The intended use of the carrier (e.g., power projection, defense, or humanitarian missions) can dictate its size and capabilities. - Budget Constraints: Building and maintaining an aircraft carrier is extremely costly, and budget limitations can influence the size and features of the vessel.
Operational Considerations

The size of an aircraft carrier has significant operational implications: - Air Wing Size: Larger carriers can support larger air wings, providing more flexibility and capability in combat operations. - Endurance and Range: The size of a carrier can affect its endurance at sea and its range, influencing how long it can stay in an operational area without resupply. - Defense Capabilities: The defensive systems and armament of a carrier are also influenced by its size, with larger carriers typically having more robust defenses.
🚨 Note: The operational effectiveness of an aircraft carrier is not solely determined by its size. Technological advancements, crew training, and strategic deployment are equally important factors.
Future Developments in Aircraft Carrier Design

The design and construction of aircraft carriers are continually evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing military requirements, and the need for more efficient and cost-effective vessels. Future developments may include: - Electric Propulsion: More efficient and quieter propulsion systems. - Advanced Materials: The use of lighter and stronger materials to reduce size and increase capability. - Unmanned Aircraft: Integration of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) into carrier operations, potentially reducing the need for manned aircraft. - Modular Design: Designing carriers with modular components to facilitate easier upgrade and repair.
Global Implications

The size and capability of aircraft carriers have significant implications for global security and geopolitical dynamics. They represent a formidable military capability that can project power across the globe. The acquisition and development of aircraft carriers by various nations are closely watched, as they can signal shifts in military balance and strategic intentions.
To wrap things up, the size of an aircraft carrier is a critical aspect of its capability and reflects a nation’s military strategy and technological prowess. As naval technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see innovations in aircraft carrier design that enhance their operational effectiveness while potentially reducing their size and environmental impact.
What is the purpose of an aircraft carrier?
+
An aircraft carrier serves as a mobile airbase that can deploy aircraft for various military operations, including power projection, defense, and humanitarian missions.
Which country has the most aircraft carriers?
+
The United States has the largest number of aircraft carriers, with both conventional and nuclear-powered vessels in its fleet.
How long does it take to build an aircraft carrier?
+
The construction time for an aircraft carrier can vary significantly, typically ranging from 5 to 15 years, depending on the complexity of the design and the resources available.
