Military
American Soldier Salary Per Month

Introduction to American Soldier Salaries
The salaries of American soldiers vary based on their rank, time in service, and other factors. Understanding the compensation structure is essential for those considering a career in the military. The salary is not just about the monthly pay but also includes benefits, allowances, and special pays that can significantly impact the total compensation package.
Basic Pay Scale

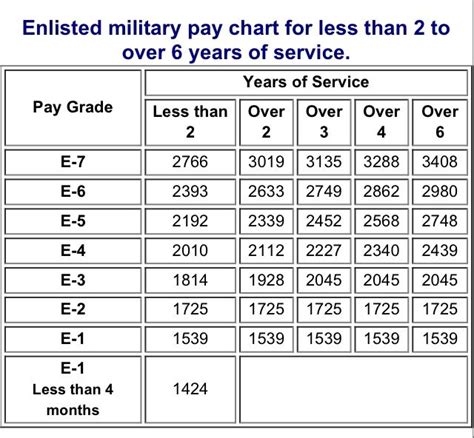
The basic pay scale for American soldiers is divided into two main categories: enlisted personnel and officers. The pay scales are as follows: - Enlisted Personnel: Ranks from Private (E-1) to Sergeant Major of the Army (E-9). - Officers: Ranks from Second Lieutenant (O-1) to General (O-10).
Monthly Salary Ranges

Here is a general overview of the monthly salary ranges for American soldiers, based on 2023 data: - Private (E-1): Approximately 1,733 per month. - Private First Class (E-2): Approximately 1,942 per month. - Specialist/Corporal (E-4): Approximately 2,515 per month. - Sergeant (E-5): Approximately 2,871 per month. - Staff Sergeant (E-6): Approximately 3,208 per month. - Second Lieutenant (O-1): Approximately 3,287 per month. - First Lieutenant (O-2): Approximately 3,787 per month. - Captain (O-3): Approximately 4,637 per month.
Factors Affecting Salary

Several factors can affect the monthly salary of an American soldier: - Time in Service: The longer a soldier serves, the higher their pay will be within their rank. - Rank: Advancing in rank significantly increases salary. - Special Duty Pay: Soldiers in certain specialties or performing hazardous duties may receive additional pay. - Allowances: Soldiers may receive allowances for housing, food, and clothing, which can be substantial. - Education Benefits: Soldiers can receive education benefits, including tuition assistance and the GI Bill.
Benefits and Allowances
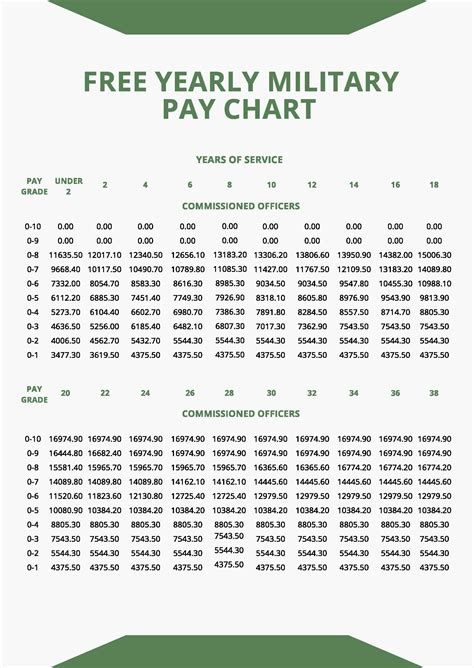
Beyond the basic pay, American soldiers receive a range of benefits and allowances that can significantly increase their total compensation: - Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): Varies by location but can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars per month. - Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): Approximately 369 per month for enlisted personnel and 287 for officers. - Health Insurance: Soldiers and their families receive comprehensive health insurance. - Education Benefits: Soldiers can use the GI Bill to fund their education after service.
Special Pays

Certain situations or roles within the military can qualify soldiers for special pays: - Hazardous Duty Pay: For duties that involve unusual hazards. - Flight Pay: For pilots and aircrew members. - Jump Pay: For paratroopers. - Dive Pay: For soldiers who are divers.
📝 Note: These figures are subject to change and may not reflect the current pay scale. Always check the most recent data from official military sources for the most accurate information.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In summary, the salary of an American soldier is influenced by a variety of factors including rank, time in service, and special duties. While the basic pay provides a foundation, it is the combination of pay, allowances, benefits, and special pays that truly reflects the compensation for serving in the military. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone considering a military career, as it impacts not just the immediate financial situation but also long-term benefits and opportunities.
What is the starting salary for an American soldier?
+The starting salary for an American soldier, typically at the rank of Private (E-1), is approximately $1,733 per month, though this can vary based on the current pay scale.
How does rank affect salary in the military?
+Advancing in rank directly impacts salary, with higher ranks receiving significantly more pay. Each rank has a set pay range that also increases with time in service.
What benefits are included in the total compensation package for American soldiers?
+Beyond basic pay, American soldiers receive benefits such as housing and food allowances, comprehensive health insurance, education benefits, and potentially special duty pay, among others.