Army Junior Rotc Ranks
Understanding the Army Junior ROTC Ranks

The Army Junior Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (JROTC) is a program designed to instill leadership skills, discipline, and a sense of responsibility in high school students. It offers a unique opportunity for young individuals to explore military-style training and gain valuable life skills. One of the key aspects of JROTC is its rank structure, which mirrors the hierarchy found in the US Army. In this blog post, we will delve into the ranks of the Army Junior ROTC, exploring the responsibilities, qualifications, and promotions within this program.
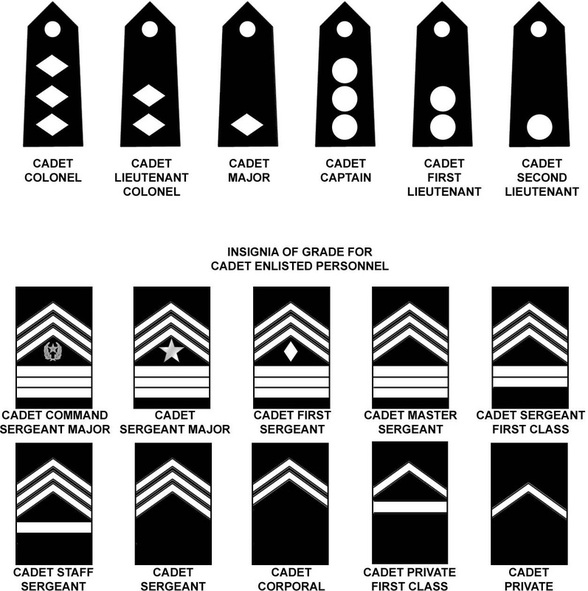
Enlisted Ranks
The enlisted ranks in Army Junior ROTC form the backbone of the program, as they are the ones who actively participate in training and lead their peers. These ranks are divided into four main categories: Private, Corporal, Sergeant, and Staff Sergeant.
Private (PV1)
- Responsibilities: Privates are the entry-level rank in JROTC. They are typically new members who are still learning the basics of military discipline and leadership. Privates are expected to follow orders, maintain a high standard of personal appearance, and demonstrate a strong work ethic.
- Qualifications: To become a Private, students must enroll in the JROTC program and complete the basic training course. This rank is open to all students, regardless of their prior experience or knowledge of military affairs.
Corporal (CPL)
- Responsibilities: Corporals are the first step up in the enlisted ranks. They serve as team leaders and are responsible for guiding and mentoring Privates. Corporals are expected to demonstrate leadership skills, maintain discipline within their team, and assist in training activities.
- Qualifications: Promotion to Corporal is usually based on a combination of factors, including academic performance, leadership potential, and participation in JROTC events. Students must display a strong commitment to the program and exhibit the qualities necessary for effective leadership.
Sergeant (SGT)
- Responsibilities: Sergeants are key leaders within the JROTC unit. They oversee multiple teams and are responsible for ensuring the smooth operation of training activities. Sergeants play a crucial role in mentoring junior members and fostering a positive learning environment.
- Qualifications: Promotion to Sergeant is highly competitive and requires exceptional leadership skills. Candidates for this rank must demonstrate a deep understanding of JROTC principles, exceptional academic performance, and a proven track record of successful leadership experiences.
Staff Sergeant (SSG)
- Responsibilities: Staff Sergeants are the highest-ranking enlisted members in JROTC. They serve as the right-hand of the Cadet Commander and are responsible for the overall administration and discipline of the unit. Staff Sergeants play a vital role in training and mentoring junior members, ensuring the smooth functioning of the program.
- Qualifications: Reaching the rank of Staff Sergeant is a significant achievement in JROTC. Candidates must possess exceptional leadership abilities, a strong understanding of military customs and courtesies, and a proven record of successful leadership experiences. Staff Sergeants are often chosen based on their ability to inspire and motivate others.
Officer Ranks
In addition to the enlisted ranks, Army Junior ROTC also has a separate officer rank structure. These ranks are reserved for students who have demonstrated exceptional leadership qualities and have been selected to lead the entire unit.
Cadet Commander (CC)
- Responsibilities: The Cadet Commander is the highest-ranking individual in the JROTC unit. They are responsible for the overall management and administration of the program, including planning and executing training activities, leading parades, and representing the unit in official ceremonies.
- Qualifications: Becoming a Cadet Commander is a prestigious honor and requires exceptional leadership skills, academic excellence, and a deep understanding of JROTC principles. Candidates must undergo a rigorous selection process, which often includes interviews, written examinations, and assessments of their leadership potential.
Cadet Executive Officer (CXO)
- Responsibilities: The Cadet Executive Officer serves as the second-in-command to the Cadet Commander. They assist in the day-to-day operations of the unit, oversee the performance of staff members, and ensure the smooth functioning of the program.
- Qualifications: Promotion to Cadet Executive Officer is based on leadership potential, academic performance, and a proven track record of successful leadership experiences. Candidates must demonstrate exceptional organizational skills, the ability to make sound decisions, and a commitment to the well-being of their fellow cadets.
Cadet Company Commander (CCC)
- Responsibilities: Cadet Company Commanders lead individual companies within the JROTC unit. They are responsible for the training and discipline of their company, ensuring that all members adhere to the program’s standards and regulations.
- Qualifications: Promotion to Cadet Company Commander is highly competitive and requires exceptional leadership skills, a strong understanding of military tactics, and a proven ability to lead and motivate others. Candidates must demonstrate a deep commitment to the JROTC program and a willingness to take on additional responsibilities.
Cadet Platoon Leader (CPL)
- Responsibilities: Cadet Platoon Leaders are responsible for leading and training their assigned platoons. They oversee the daily activities of their platoon, ensure discipline, and provide guidance to junior members.
- Qualifications: Becoming a Cadet Platoon Leader requires strong leadership skills, a solid understanding of military tactics, and a commitment to the JROTC program. Candidates must be able to effectively communicate and inspire their platoon members, ensuring a cohesive and disciplined unit.
Promotions and Qualifications
Promotions within Army Junior ROTC are based on a combination of factors, including academic performance, leadership potential, and participation in JROTC activities. The program places a strong emphasis on leadership development, and promotions are often awarded to those who demonstrate exceptional qualities in this area.
Students who wish to pursue promotions must meet certain qualifications, such as maintaining a minimum GPA, participating in community service activities, and demonstrating a strong commitment to the JROTC program. Additionally, they may be required to undergo additional training or complete specific tasks to prove their readiness for higher ranks.
Table: Army Junior ROTC Ranks and Qualifications
| Rank | Responsibilities | Qualifications |
|---|---|---|
| Private (PV1) | Entry-level rank, follows orders and maintains discipline. | Enroll in JROTC and complete basic training. |
| Corporal (CPL) | Team leader, guides and mentors Privates. | Leadership potential, academic performance, and participation in JROTC events. |
| Sergeant (SGT) | Oversees multiple teams, mentors junior members. | Exceptional leadership skills, academic excellence, and successful leadership experiences. |
| Staff Sergeant (SSG) | Highest-ranking enlisted member, administers and disciplines the unit. | Exceptional leadership abilities, understanding of military customs, and a proven record of successful leadership. |
| Cadet Commander (CC) | Highest-ranking individual, manages and represents the unit. | Exceptional leadership skills, academic excellence, and a deep understanding of JROTC principles. |
| Cadet Executive Officer (CXO) | Second-in-command, assists the Cadet Commander. | Leadership potential, academic performance, and successful leadership experiences. |
| Cadet Company Commander (CCC) | Leads individual companies, ensures discipline and training. | Exceptional leadership skills, understanding of military tactics, and a commitment to JROTC. |
| Cadet Platoon Leader (CPL) | Leads and trains platoons, provides guidance to junior members. | Strong leadership skills, understanding of military tactics, and a commitment to JROTC. |

Notes

- It’s important to note that the specific qualifications and requirements for promotions may vary slightly between different JROTC units and schools.
- Promotions in JROTC are not automatic and require a rigorous selection process to ensure that only the most qualified and deserving cadets are chosen for higher ranks.
- While the JROTC program focuses on military-style training, it also emphasizes the development of leadership, discipline, and citizenship skills, which can benefit students in various aspects of their lives.
Final Thoughts

The Army Junior ROTC rank structure provides a clear path for students to develop their leadership skills and take on increasing responsibilities within the program. By progressing through the ranks, cadets gain valuable experience, learn important life lessons, and prepare themselves for future leadership roles, whether in the military or in other areas of society. The JROTC program not only equips students with practical skills but also instills a sense of discipline, teamwork, and patriotism, fostering well-rounded individuals ready to face the challenges of the future.
