Cons Of Fossil Fuels

The reliance on fossil fuels has long been a subject of debate, with a growing consensus leaning towards the need for a transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. While fossil fuels have undoubtedly played a significant role in powering our modern world, it is crucial to acknowledge their detrimental impacts on the environment and human health. In this blog post, we will delve into the various cons of fossil fuels, exploring their environmental, economic, and social implications. By understanding these drawbacks, we can better appreciate the urgency of adopting renewable energy alternatives.
Environmental Impact

The environmental consequences of fossil fuel usage are far-reaching and severe. Here are some key concerns:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Fossil fuels are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2). These gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change. The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas releases vast amounts of CO2, contributing to the rapid increase in global temperatures.
- Air Pollution: The combustion of fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants into the air. These pollutants include nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Air pollution caused by fossil fuels is a major contributor to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and premature deaths.
- Water Pollution: Fossil fuel extraction and processing can contaminate water sources. Oil spills, for instance, can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems, leading to the death of marine life and the disruption of entire food chains. Additionally, the use of chemicals in the extraction process, such as fracking fluids, can leach into groundwater, posing risks to human health and the environment.
- Land Degradation: The extraction of fossil fuels often requires extensive land use, leading to deforestation, habitat destruction, and the disruption of natural ecosystems. Open-pit mining, strip mining, and mountaintop removal for coal extraction are particularly destructive, leaving behind scarred landscapes and degraded ecosystems.
Economic Disadvantages

While fossil fuels have been a cornerstone of the global economy for decades, their economic disadvantages are becoming increasingly evident:
- Volatile Energy Prices: The price of fossil fuels is subject to significant fluctuations due to various factors, including geopolitical tensions, supply disruptions, and market speculation. These price volatility can have far-reaching economic consequences, affecting industries, businesses, and households alike.
- Resource Depletion: Fossil fuels are finite resources, and their rapid depletion poses a long-term economic challenge. As easily accessible reserves are exhausted, the cost of extraction increases, leading to higher energy prices and potential energy shortages.
- Healthcare Costs: The negative health impacts associated with fossil fuel pollution result in substantial healthcare costs. Treating respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and other health issues linked to air and water pollution puts a strain on healthcare systems and increases the financial burden on individuals and governments.
- Infrastructure Costs: The infrastructure required to transport and distribute fossil fuels, such as pipelines, refineries, and power plants, comes with significant capital and maintenance costs. These costs are often borne by taxpayers and can hinder the development of more sustainable and decentralized energy systems.
Social and Ethical Concerns

The use of fossil fuels also raises important social and ethical considerations:
- Inequality and Energy Access: The distribution of fossil fuel resources is often uneven, leading to energy inequality. Many communities, particularly in developing countries, lack access to reliable and affordable energy sources. This inequality perpetuates poverty and hinders social and economic development.
- Human Rights Violations: The extraction of fossil fuels has been linked to human rights abuses in various parts of the world. Indigenous communities, for example, have faced displacement and the loss of their cultural heritage due to the development of fossil fuel projects on their lands.
- Climate Injustice: The impacts of climate change, largely driven by fossil fuel emissions, disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Developing countries, which have contributed the least to global emissions, often bear the brunt of climate-related disasters, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
The Way Forward
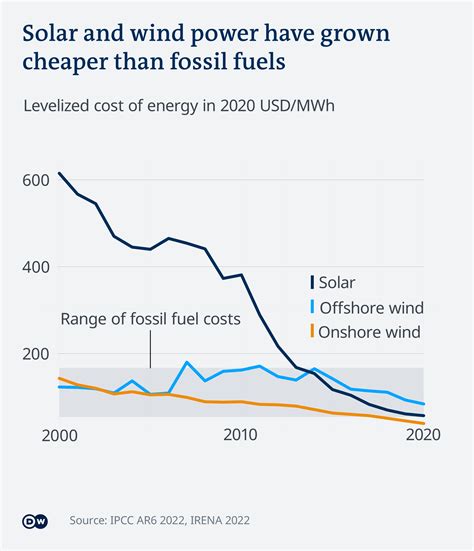
Recognizing the cons of fossil fuels is a crucial step towards transitioning to a more sustainable and equitable energy future. Here are some key takeaways:
- The environmental, economic, and social disadvantages of fossil fuels highlight the urgent need for a shift towards renewable energy sources.
- Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, offer cleaner and more sustainable alternatives with fewer negative impacts.
- Investing in renewable energy infrastructure and research can drive innovation, create jobs, and foster a more resilient and equitable energy system.
- Transitioning away from fossil fuels requires collaboration between governments, industries, and individuals. Policies and incentives that support renewable energy adoption are essential to accelerate this transition.
By understanding the cons of fossil fuels and embracing the opportunities presented by renewable energy, we can work towards a future where clean and sustainable energy sources power our lives without compromising the health of our planet and its inhabitants.
What are the main environmental impacts of fossil fuels?
+The environmental impacts of fossil fuels include greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, land degradation, and the disruption of natural ecosystems.
How do fossil fuels contribute to climate change?
+Fossil fuels are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2). These emissions trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change.
What are the economic disadvantages of relying on fossil fuels?
+Economic disadvantages include volatile energy prices, resource depletion, high healthcare costs due to pollution-related illnesses, and infrastructure costs associated with fossil fuel infrastructure.
How do fossil fuels impact social and ethical considerations?
+Fossil fuels contribute to energy inequality, human rights violations, and climate injustice. The uneven distribution of fossil fuel resources and the impacts of climate change disproportionately affect vulnerable communities.
What are the alternatives to fossil fuels?
+Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal offer cleaner and more sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. These technologies have the potential to power our future without the negative environmental and social impacts.


