Kelvin Explained: The Essential Guide To Understanding Temperature

Understanding temperature is crucial in various fields, from science and engineering to everyday life. Among the many temperature scales, Kelvin stands out as a fundamental unit of measurement. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Kelvin, exploring its history, significance, and practical applications.
The Birth of Kelvin: A Brief History

The Kelvin temperature scale owes its existence to the brilliant mind of William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin. Born in 1824, Lord Kelvin was a renowned British physicist and engineer who made significant contributions to the fields of thermodynamics and electromagnetism. It was his vision to create a temperature scale that would eliminate the limitations of the existing Celsius and Fahrenheit scales.
Lord Kelvin's motivation was twofold. Firstly, he aimed to establish a temperature scale that started from absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature where molecular motion ceases. Secondly, he wanted a scale that would be consistent with the second law of thermodynamics, ensuring a smooth and logical progression of temperature values.
In 1848, Lord Kelvin proposed his temperature scale, initially known as the "absolute temperature scale." This scale set absolute zero as its starting point, with each degree representing an equal interval of temperature change. The scale was later renamed in his honor, becoming the Kelvin scale we know today.
Understanding the Kelvin Scale

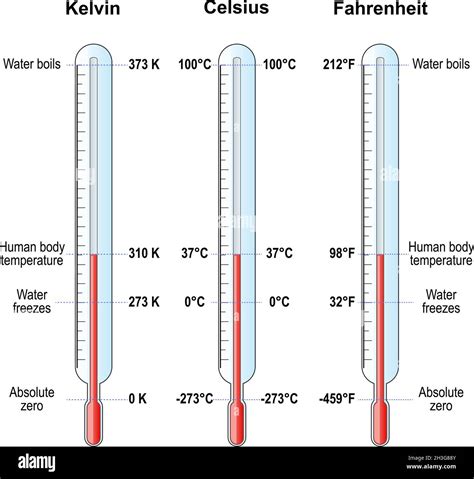
The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale, meaning it measures temperature from absolute zero, denoted as 0 K. This scale is based on the behavior of ideal gases and is intrinsically linked to the concept of thermal energy.
Here are some key characteristics of the Kelvin scale:
- Absolute Zero: The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, which is approximately -273.15°C or -459.67°F. This temperature represents the point at which all thermal motion ceases, and molecules have minimal kinetic energy.
- Equal Intervals: Each degree on the Kelvin scale represents an equal change in temperature. This makes it a highly accurate and consistent measurement system, especially when dealing with scientific and engineering applications.
- Celsius Conversion: The Kelvin scale is directly related to the Celsius scale. To convert a temperature from Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273.15 to the Celsius value. For example, 0°C is equal to 273.15 K.
- Fahrenheit Conversion: Converting temperatures from Fahrenheit to Kelvin involves a more complex calculation. The formula is: K = (°F + 459.67) / 1.8.
The Significance of Kelvin
The Kelvin scale holds immense importance in various scientific and industrial domains. Here are some key reasons why understanding Kelvin is essential:
- Scientific Research: Kelvin is the primary temperature scale used in scientific research, especially in fields like physics, chemistry, and astronomy. It allows scientists to accurately measure and compare temperatures across different experiments and phenomena.
- Thermodynamics: The Kelvin scale is intimately connected to the principles of thermodynamics. It helps scientists and engineers understand and analyze heat transfer, energy conversion, and the behavior of gases and fluids.
- Engineering Applications: Engineers rely on the Kelvin scale when designing and optimizing systems, such as refrigeration, air conditioning, and power generation. Accurate temperature measurement is crucial for ensuring efficiency and safety in these applications.
- Astronomy and Space Exploration: In the vastness of space, where temperatures can vary dramatically, the Kelvin scale is indispensable. It helps astronomers and space scientists study celestial bodies, measure the temperature of stars, and understand the thermal properties of planets and other cosmic objects.
Practical Applications of Kelvin
The Kelvin scale finds practical applications in numerous everyday scenarios. Here are some examples:
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists often use the Kelvin scale to analyze and predict weather patterns. By measuring temperature variations in the atmosphere, they can make more accurate forecasts and understand the behavior of weather systems.
- Food Safety: In the food industry, maintaining proper temperatures is crucial for food safety and preservation. The Kelvin scale helps ensure that refrigeration and freezing systems operate within the required temperature ranges to prevent bacterial growth and food spoilage.
- Automotive Engineering: Engine performance and efficiency are closely tied to temperature. Automotive engineers use the Kelvin scale to monitor and optimize engine temperatures, ensuring optimal combustion and minimizing wear and tear.
- Medical Applications: In the medical field, precise temperature control is essential for various procedures and treatments. The Kelvin scale is used in medical research, diagnostic imaging, and therapeutic applications to maintain accurate temperature conditions.
Converting Between Temperature Scales

While the Kelvin scale is the preferred choice for scientific and engineering purposes, it is essential to understand how to convert temperatures between different scales. Here are the formulas for common temperature conversions:
| From | To | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Celsius | Kelvin | K = °C + 273.15 |
| Fahrenheit | Kelvin | K = (°F + 459.67) / 1.8 |
| Kelvin | Celsius | °C = K - 273.15 |
| Kelvin | Fahrenheit | °F = 1.8 * K - 459.67 |

⚠️ Note: When converting temperatures, ensure that you use the correct units and formulas to obtain accurate results.
Common Misconceptions About Kelvin

Despite its widespread use, there are a few misconceptions about the Kelvin scale that are worth clarifying:
- Kelvin vs. Celsius: Some people mistakenly believe that Kelvin is simply Celsius minus 273.15. While it is true that the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, each degree on the Kelvin scale represents an equal interval of temperature change, making it a distinct and unique scale.
- Negative Temperatures: Unlike the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, the Kelvin scale does not have negative values. Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature, and any temperature below it is not physically realizable.
The Future of Temperature Measurement

As technology advances, so do the methods and tools for temperature measurement. Here are some emerging trends and innovations in temperature measurement:
- Smart Sensors: The development of smart sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices has revolutionized temperature monitoring. These sensors can provide real-time data, allowing for remote temperature control and alerting systems.
- Quantum Thermometry: Researchers are exploring quantum-based thermometry techniques, which offer unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity. These methods have the potential to revolutionize temperature measurement in various scientific and industrial applications.
- Non-Contact Temperature Measurement: Non-contact temperature measurement devices, such as infrared thermometers, are becoming increasingly popular. These tools allow for quick and accurate temperature readings without physical contact, making them ideal for industrial and medical applications.
Final Thoughts

Understanding the Kelvin temperature scale is not only fascinating but also crucial for anyone involved in scientific, engineering, or industrial fields. Its absolute nature and consistent intervals make it an indispensable tool for accurate temperature measurement and analysis. From the depths of space to the intricate workings of engines, the Kelvin scale plays a vital role in shaping our understanding of the world around us.
As we continue to explore and innovate, temperature measurement will remain a fundamental aspect of our scientific and technological endeavors. By embracing the power of Kelvin and staying updated with the latest advancements, we can unlock new possibilities and push the boundaries of what we know and understand.
What is the lowest possible temperature in Kelvin?
+The lowest possible temperature in Kelvin is absolute zero, which is approximately 0 K. This temperature represents the point at which molecular motion ceases, and no thermal energy exists.
Why is the Kelvin scale preferred in scientific research?
+The Kelvin scale is preferred in scientific research because it is an absolute temperature scale, starting from absolute zero. This makes it ideal for precise temperature measurements and comparisons across different experiments and phenomena.
Can negative temperatures exist in Kelvin?
+No, negative temperatures do not exist in Kelvin. The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, and any temperature below it is not physically realizable.

