Lung Nodules After Covid19

The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has brought about numerous health concerns, and one of the post-infection complications that has gained attention is the presence of lung nodules. Lung nodules are small, roundish growths that develop in the lungs, and while they are often benign, they can sometimes be a cause for concern. In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of lung nodules after COVID-19, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
Understanding Lung Nodules

Lung nodules, also known as pulmonary nodules, are small masses or lesions that typically measure less than 3 centimeters in diameter. They can develop in one or both lungs and are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans. Lung nodules can be classified into two main categories:
- Benign Lung Nodules: These nodules are non-cancerous and are usually caused by scar tissue, inflammation, or infections. They often remain stable or resolve on their own over time.
- Malignant Lung Nodules: Malignant nodules are cancerous and can be a sign of lung cancer or metastasis from other cancer types. These nodules require prompt attention and treatment.
Lung Nodules and COVID-19
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, primarily affects the respiratory system, leading to a range of symptoms, including cough, shortness of breath, and pneumonia. In some cases, individuals who have recovered from COVID-19 may develop lung nodules as a post-infection complication.
Causes of Lung Nodules After COVID-19
The exact cause of lung nodules following COVID-19 infection is not fully understood. However, several factors may contribute to their development:
- Inflammation and Scarring: COVID-19 can cause significant inflammation in the lungs, leading to tissue damage and scarring. Over time, this scarring may result in the formation of lung nodules.
- Persistent Infection: In some cases, the SARS-CoV-2 virus may persist in the lungs even after the initial infection has resolved. This persistent infection can trigger an immune response, potentially leading to the development of nodules.
- Immune System Dysfunction: COVID-19 can disrupt the immune system's normal functioning, causing an overactive or dysregulated immune response. This dysregulation may contribute to the formation of lung nodules.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Lung nodules themselves often do not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, individuals who have experienced severe COVID-19 symptoms or have a history of lung issues may be more likely to develop nodules with symptoms. Common symptoms associated with lung nodules include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue and weakness
- Wheezing or abnormal breathing sounds
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. The diagnosis of lung nodules typically involves the following steps:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your medical history, including any previous COVID-19 infection, and perform a physical examination to assess your overall health.
- Imaging Tests: Chest X-rays and CT scans are commonly used to visualize the lungs and detect the presence of nodules. These imaging tests can provide detailed information about the size, location, and characteristics of the nodules.
- Further Investigations: Depending on the findings of the initial imaging tests, your doctor may recommend additional tests such as pulmonary function tests, bronchoscopy, or biopsy to determine the nature of the nodules and rule out any underlying conditions.
Management and Treatment

The management and treatment of lung nodules after COVID-19 depend on various factors, including the size, growth rate, and characteristics of the nodules, as well as the individual's overall health and medical history.
Monitoring and Observation
For small, benign lung nodules that are not causing any symptoms, the recommended approach is often close monitoring and observation. This involves regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests to track the size and growth of the nodules over time. If the nodules remain stable or show no signs of growth, further intervention may not be necessary.
Medical Treatment
In cases where lung nodules are causing symptoms or there is a concern for malignancy, medical treatment may be required. The specific treatment approach will depend on the underlying cause of the nodules. Some common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: If the nodules are caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the bacteria or other pathogens.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Medications such as corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms associated with lung nodules.
- Bronchodilators: These medications are used to relax the muscles around the airways, improving breathing and reducing symptoms like shortness of breath.
Surgical Intervention
In cases where lung nodules are malignant or there is a high suspicion of cancer, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include:
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): This minimally invasive procedure involves the removal of the lung nodule through small incisions, using a camera and specialized instruments.
- Open Thoracotomy: In more complex cases or when the nodule is located deep within the lung, an open surgical approach may be required. This involves a larger incision to access and remove the nodule.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
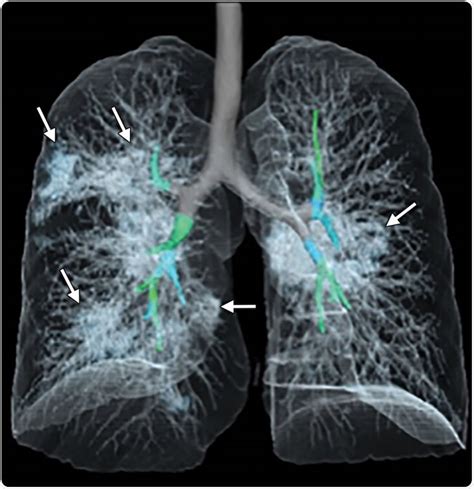
While it may not be possible to completely prevent the development of lung nodules after COVID-19, certain measures can help reduce the risk and promote overall lung health:
- Vaccination: Staying up-to-date with COVID-19 vaccinations can help prevent severe infections and reduce the risk of long-term complications, including lung nodules.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, can support lung health and reduce the risk of respiratory issues.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups and follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential, especially if you have a history of COVID-19 infection or lung issues. Early detection and management of lung nodules can improve outcomes.
Conclusion
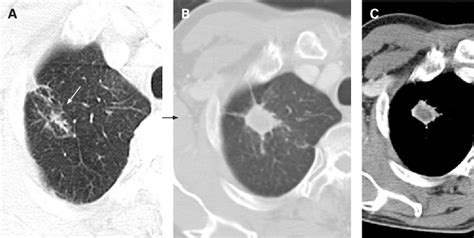
Lung nodules after COVID-19 are a concerning complication that requires proper evaluation and management. While many lung nodules are benign and may not require immediate treatment, close monitoring and follow-up care are essential. By staying informed, seeking timely medical attention, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their lung health and address any potential issues associated with lung nodules.
Are lung nodules always cancerous after COVID-19 infection?
+No, lung nodules after COVID-19 are often benign and non-cancerous. However, it is important to have them evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine their nature and rule out any potential concerns.
How often should I get imaging tests to monitor lung nodules after COVID-19?
+The frequency of imaging tests depends on the size, growth rate, and characteristics of the lung nodules. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate monitoring schedule based on your individual case.
Can lung nodules after COVID-19 resolve on their own?
+Yes, in some cases, small and benign lung nodules may resolve on their own over time. However, it is important to have them monitored by a healthcare professional to ensure they do not grow or cause any complications.
What are the long-term effects of lung nodules after COVID-19?
+The long-term effects of lung nodules after COVID-19 can vary. In most cases, benign nodules do not cause significant long-term issues. However, malignant nodules may require ongoing treatment and management to prevent the spread of cancer.
Is it normal to experience breathing difficulties after COVID-19 due to lung nodules?
+Breathing difficulties can be a symptom of lung nodules, especially if they are causing inflammation or obstruction in the airways. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
