Ultimate Guide: Chapter 11 Vs 7 Differences

Chapter 11 and Chapter 7: Unraveling the Differences
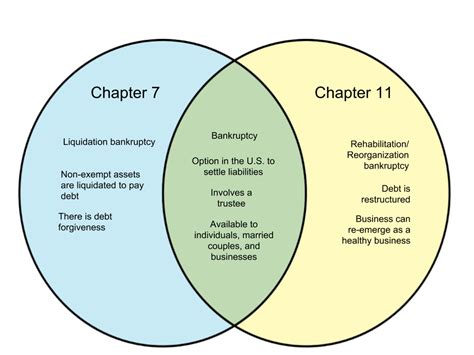
In the realm of bankruptcy law, Chapters 11 and 7 are two distinct paths that individuals and businesses can take when facing financial difficulties. While both options provide a means to address debt and financial distress, they differ significantly in their approach, outcomes, and suitability for different situations. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key differences between Chapter 11 and Chapter 7, helping you understand which option might be more advantageous for your specific circumstances.
Understanding Chapter 11
Chapter 11, often referred to as “reorganization” or “rehabilitation,” is a powerful tool designed to help businesses restructure their finances and emerge stronger. It allows debtors, typically businesses or high-net-worth individuals, to propose a plan to repay their creditors while continuing to operate and make necessary adjustments to their operations. This chapter provides a unique opportunity for businesses to regain financial stability and potentially thrive again.
Key Features of Chapter 11:
- Continued Operation: Debtors can continue to operate their business under court supervision, making necessary adjustments to improve profitability.
- Debt Restructuring: Chapter 11 enables debtors to negotiate with creditors, potentially reducing or modifying debt obligations.
- Flexibility: The process offers flexibility in creating a repayment plan tailored to the debtor’s specific needs and circumstances.
- Asset Protection: Businesses can protect their valuable assets and continue operations, preventing liquidation.
- Complex Procedure: Chapter 11 cases can be intricate and time-consuming, often requiring legal expertise and strategic planning.
Chapter 7: A Different Approach
Chapter 7, known as “liquidation,” takes a different path by focusing on the sale of assets to repay creditors. It is a faster and more straightforward process, making it suitable for individuals or businesses with limited assets or those seeking a quick resolution to their financial troubles. Chapter 7 offers a fresh start by discharging most debts, allowing individuals or businesses to move forward with a clean slate.
Key Aspects of Chapter 7:
- Asset Liquidation: Debtors must surrender non-exempt assets, which are then sold to repay creditors.
- Debt Discharge: Upon completion of the process, most debts are discharged, providing a fresh financial beginning.
- Quick Resolution: Chapter 7 cases are typically resolved within a few months, offering a rapid solution.
- Eligibility: Individuals, sole proprietors, and some small businesses are eligible for Chapter 7.
- Limited Asset Protection: Debtors may keep certain exempt assets, but the process generally involves liquidating non-exempt property.
Comparing the Two Chapters:
| Chapter 11 | Chapter 7 |
|---|---|
📈 Focuses on business reorganization and continued operation. |
🗑️ Emphasizes asset liquidation and debt discharge. |
🛠️ Allows for debt restructuring and negotiation. |
🔄 Provides a quick and efficient resolution. |
🎯 Suitable for businesses aiming to regain financial stability. |
🧰 Ideal for individuals or businesses with limited assets. |
⏰ Lengthy and complex process. |
⏱️ Quick and straightforward procedure. |
🛡️ Protects valuable business assets. |
🛑 Involves surrendering non-exempt assets. |

When to Choose Chapter 11:
- Viable Business: If your business has a solid foundation and the potential for profitability, Chapter 11 can help restructure finances and maintain operations.
- Complex Financial Situation: When dealing with intricate financial matters, Chapter 11 provides the flexibility to negotiate and create a tailored repayment plan.
- Asset Protection: For businesses with valuable assets, Chapter 11 offers a way to protect these assets while addressing debt.
When to Opt for Chapter 7:
- Limited Assets: If you have few assets or no valuable property, Chapter 7 allows for a quick resolution without sacrificing essential possessions.
- Overwhelming Debt: When facing unmanageable debt and seeking a fresh start, Chapter 7 provides debt discharge and a new financial beginning.
- Simplicity: For those seeking a straightforward and rapid solution, Chapter 7 offers a simpler process compared to Chapter 11.
The Decision-Making Process:
Choosing between Chapter 11 and Chapter 7 is a critical decision that requires careful consideration. It is essential to evaluate your financial situation, goals, and the nature of your debt. Consulting with a bankruptcy attorney who specializes in these chapters can provide valuable guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Notes:
⚖️
Legal Advice: It is crucial to seek professional legal counsel to understand the implications and requirements of each chapter.🌐
Research: Explore reputable online resources and educational materials to gain a deeper understanding of bankruptcy options.📚
Case Studies: Study real-life examples of businesses or individuals who have successfully navigated Chapter 11 or Chapter 7 to gain insights.
Conclusion:
Understanding the differences between Chapter 11 and Chapter 7 is a crucial step in navigating the complex world of bankruptcy. Whether you aim to reorganize your business or seek a fresh financial start, choosing the right chapter can significantly impact your future. Remember, each case is unique, and seeking expert advice is essential to make an informed decision.
FAQ
Can I switch from Chapter 11 to Chapter 7 or vice versa?
+Yes, it is possible to convert from one chapter to another under certain circumstances. Consult with a bankruptcy attorney to understand the specific requirements and implications of such a conversion.
Are there any alternatives to Chapter 11 and Chapter 7?
+Yes, depending on your situation, other options like Chapter 13 (for individuals) or out-of-court settlements may be available. Exploring these alternatives is essential to find the best fit for your financial needs.
How long does the Chapter 11 process typically take?
+The duration of a Chapter 11 case can vary widely, often taking several months to a year or more. The complexity of the case and the court’s workload can influence the timeline.
What happens to my credit score during and after bankruptcy?
+Filing for bankruptcy will have a significant impact on your credit score. It will remain on your credit report for a certain period, typically 7-10 years, affecting your ability to obtain credit during that time. However, it can provide a fresh start and a chance to rebuild your financial reputation.

