What Is A Net Force

Net force is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of mechanics, that plays a crucial role in understanding the motion of objects. It refers to the combined effect of all the forces acting on an object, and it determines whether an object will accelerate, decelerate, or remain at a constant velocity.
Understanding Net Force

When multiple forces act on an object, they can either work together or oppose each other. Net force is the vector sum of these individual forces. It takes into account both the magnitude and direction of each force, allowing us to analyze the overall effect on the object's motion.
For instance, consider a book lying on a table. The table exerts an upward force (known as the normal force) to counteract the force of gravity pulling the book downward. These two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, resulting in a net force of zero. Consequently, the book remains at rest on the table.
Calculating Net Force

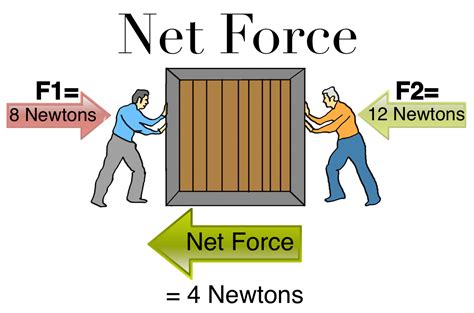
To calculate the net force on an object, you simply add up the individual forces acting on it. However, it's important to consider the direction of each force. Forces in the same direction are added together, while forces in opposite directions are subtracted.
Let's illustrate this with an example. Imagine a car accelerating forward. The engine exerts a forward force, while friction and air resistance act in the opposite direction. To find the net force, you would subtract the opposing forces from the forward force. If the net force is positive, the car will accelerate; if it's negative, the car will decelerate.
Types of Net Force

Net force can be categorized into two main types: balanced and unbalanced.
Balanced Net Force
When the net force on an object is zero, it is said to be in a state of equilibrium. This means that the forces acting on the object are balanced, and the object remains at rest or continues to move with a constant velocity. In our book-on-a-table example, the normal force and the force of gravity balance each other out, resulting in a balanced net force.
Unbalanced Net Force
An unbalanced net force occurs when the forces acting on an object are not equal and opposite. In this case, the object will experience acceleration in the direction of the net force. This acceleration can be in any direction, depending on the nature of the forces involved.
For example, when you push a shopping cart forward, your applied force is greater than the opposing forces of friction and air resistance. As a result, the net force is positive, and the cart accelerates in the direction you're pushing it.
Net Force and Newton's Second Law

Net force is closely related to Newton's Second Law of Motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This law is represented by the equation:
Fnet = m * a
Where:
- Fnet is the net force.
- m is the mass of the object.
- a is the acceleration of the object.
This equation highlights the relationship between net force, mass, and acceleration. It tells us that an object with a larger mass requires a greater net force to produce the same acceleration as an object with a smaller mass.
Real-World Applications

Understanding net force is essential in various real-world scenarios. For instance, in engineering, knowing the net force on a structure is crucial for ensuring its stability and safety. In sports, athletes rely on their understanding of net force to optimize their performance, such as in throwing a ball or hitting a golf ball.
Additionally, net force plays a vital role in space exploration. When launching a spacecraft, engineers must calculate the net force required to overcome the Earth's gravity and propel the craft into orbit or deep space.
Key Takeaways
- Net force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
- It determines whether an object will accelerate, decelerate, or remain at a constant velocity.
- Net force can be balanced (resulting in equilibrium) or unbalanced (causing acceleration).
- Newton's Second Law relates net force, mass, and acceleration.
- Understanding net force is crucial in various fields, from engineering to sports and space exploration.
Conclusion

Net force is a fundamental concept that underpins our understanding of mechanics and the motion of objects. By analyzing the combined effect of forces, we can predict and control the behavior of objects in various scenarios. Whether it's designing safe structures, optimizing athletic performance, or exploring the cosmos, net force plays a vital role in shaping our world.
What is the difference between net force and total force?
+Net force refers to the combined effect of all forces acting on an object, considering both magnitude and direction. Total force, on the other hand, is simply the sum of the magnitudes of individual forces, without considering their directions.
How does net force affect an object’s motion?
+The net force determines whether an object will accelerate, decelerate, or remain at a constant velocity. A positive net force results in acceleration, a negative net force leads to deceleration, and a zero net force means the object will maintain its current velocity.
Can an object have a net force acting on it and still be at rest?
+Yes, an object can have a net force acting on it and still be at rest if the forces are balanced. This occurs when the object is in a state of equilibrium, and the net force is zero.
How does mass affect net force and acceleration?
+According to Newton’s Second Law, the mass of an object affects its acceleration in response to a net force. An object with a larger mass requires a greater net force to produce the same acceleration as an object with a smaller mass.
What are some real-life examples of net force in action?
+Net force is evident in everyday situations. For example, when you push a car to help it start, you’re applying a net force to overcome the opposing forces of friction and air resistance. Another example is when a rocket launches into space, the net force propels it against the force of gravity.


